Kirsten Grant, General Science co-editor
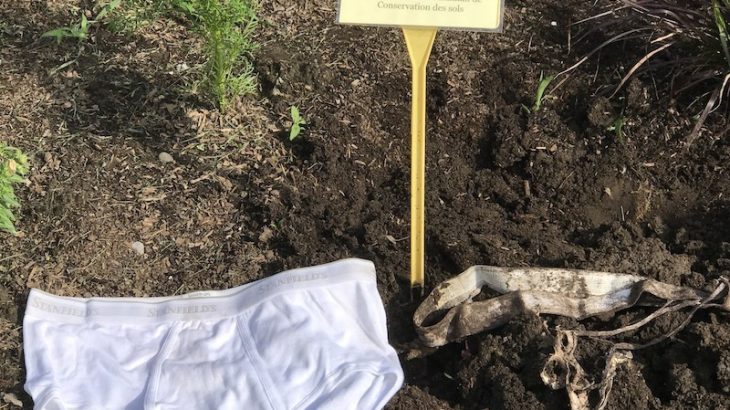
Across the country, people have been digging up buried underwear. In fact, they buried the underwear themselves to learn more about soil health as part of the Soil Your Undies campaign from the Soil Conservation Council of Canada.
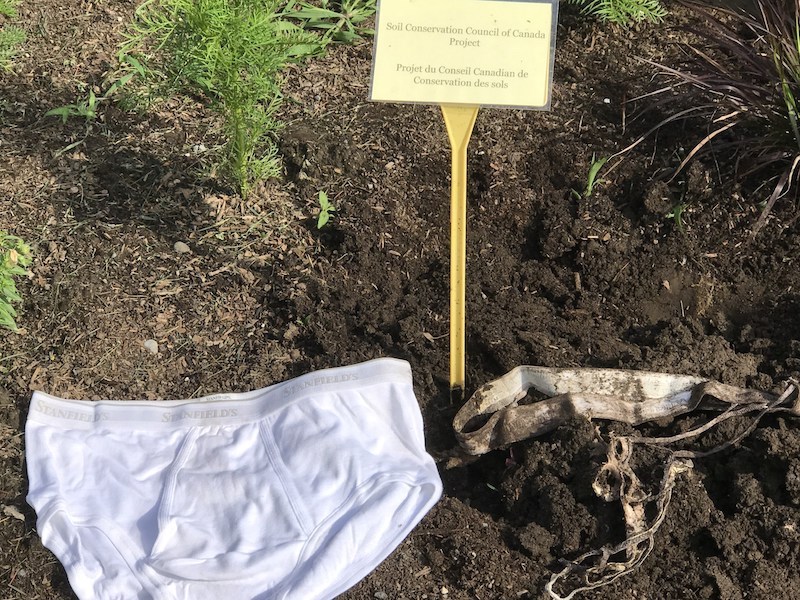

Side-by-side comparison of the Stanfield’s undies. Left – brand new undies; right – official SCCC undies that were dug up at the Canada Agriculture and Food Museum in Ottawa. (CNW Group/Soil Conservation Council of Canada (SCC))
This backyard experiment involves burying a pair of cotton underwear in the garden. Cotton underwear provides a source of carbon for the living ecosystem in the soil. Bacteria and fungi decompose the underwear over a period of two months. Then the backyard scientists dig up the underwear and recover the tattered remains, or just an elastic waistband and a few cotton scraps. This project helps people visualize the biological activity in a soil, an important part of soil health that often goes unseen.
What is soil health?
Soil is the unique and evolving product of five major components: geology, climate, topography, biology, and time. And it’s far more than just ‘dirt’: it contains an entire living ecosystem hiding just below the surface. In fact, there are over 100 million bacteria in just one teaspoon of healthy soil.
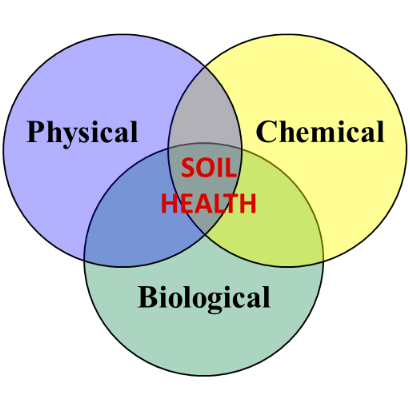
Components of soil health. Image: UMass Extension
Soil health can be broadly defined as the continued capacity of a soil to function as a living ecosystem that sustains plants, animals, and humans. It encompasses physical, chemical and biological components. While soil is developed over geological time scales, soil health considers how the soil may change over human time-scales, due to human use and management.
Why do we need healthy soils?
Soil has many important functions. The most obvious is that it supports the agricultural systems that grow our food. It’s also important for cycling and storing nitrogen and phosphorus, nutrients that are essential for life.
But aside from growing plants, did you know healthy soil also helps combat climate change? When managed well, it can help to store carbon and reduce greenhouse gas emissions. On the other hand, soil can become a source of carbon that contributesto climate change when it’s poorly managed. For example, land use change and drying of soils rich in organic matter can release carbon into the atmosphere by increasing decomposition. In addition, applying synthetic nitrogen fertilizer can also lead to greenhouse gas emissions from soil.
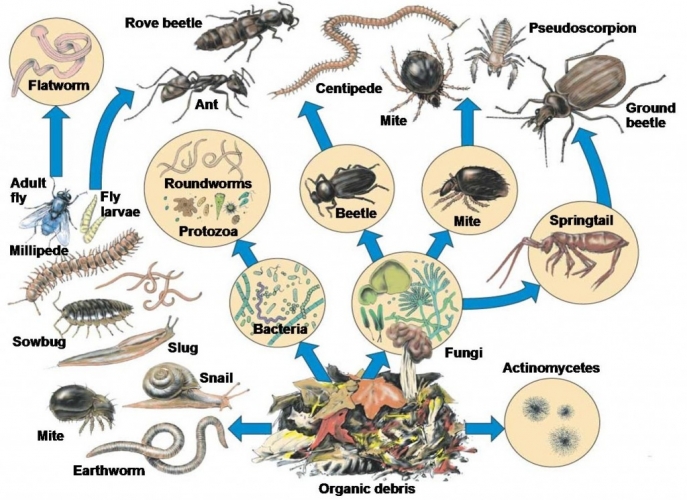
A soil food web feeding on organic debris, a source of carbon. Image: Microbes in my Soil
Healthy soil is also important for reducing the impacts of extreme weather events like floods and drought. Soil with a high proportion of organic matter can act like a sponge, absorbing and holding water. Organic matter in soil can retain about 20 times its weight in water. By quickly absorbing large amounts of water, soil can reduce the amount of water moving over its surface, limiting the impacts of floods. In turn, water stored in soil can help support plant growth during periods of drought.
What factors influence soil health?
Similar to our own health, many factors can influence soil health. These include agricultural management practices like tillage, cover crops, diverse crop rotations, and organic inputs. Shifting temperature and rainfall patterns, as a result of climate change, are also expected to influence soil health.
However, we don’t fully understand the extent and magnitude of the impacts of each of these factors. At the University of Guelph, the Soil Health Interpretive Centre (SHIC) is researching just that. This centre, the largest in North America, has 18 open-air lysimeters. Each lysimeter is an intact cylinder of soil, 1 m wide and 1.5 m deep, hooked up with sensors and placed back into the ground. SHIC allows researchers to monitor changes in water and gases year-round, under real environmental conditions. Understanding these changes will help us determine what influences soil health, and how management practices may improve it.
Shifting conversation: soil degradation to soil health
Historically, the conversation around soil has been related to soil degradation and erosion, as seen in the 1984 report Soils at Risk: Canada’s Eroding Future. By clearing forests and grasslands for our own use, we have exposed soil to erosion by wind and water. Since the 1980s, risk of soil erosion in Canada has been declining, as more farmers have shifted to less intensive tillage practices.
In the mid-1990s, language around soil began to shift from ‘soil degradation’ to ‘soil health.’ This shift has changed the focus to the quality and function of soil, instead of just its presence or absence. In turn, soil microbiology is a key component of current soil health research, as soil microbes influence its physical and chemical functions.
Since the 2015 International Year of Soils, momentum around soil health in Canada has continued to grow. This year, Ontario launched its new soil health and conservation strategy for the province, furthering the commitment to conserving and managing soil for agricultural, economic, and environmental uses.
Sharing Knowledge
With growing interest in soil, groups of producers, like the Ontario Soil Network, Saskatchewan Soil Conservation Association, and Innovative Farmers of Ontario, have emerged to increase public awareness of soil conservation and share their knowledge. These groups provide a network for growers who share trials and successes in managing their soil. They also share photos of ragged underwear dug up from their fields, as an informal way to investigate how their on-farm management practices influence biological activity and underwear decomposition.
Try it yourself!
Want to see what bacteria and fungi in your backyard are doing? Try the Soil Your Undies experiment yourself. And join the soil health conversation by sharing your results on social media using the hashtag #SoilYourUndies. Together, we can start to grasp how conditions in our own backyards can affect soil health and its role in our future.
~30~




